-
-
Latin alphabet is the basis of alphabetic systems of different West-European
languages, and in particular English or French, Italian or Spanish, Portuguese
or German. Some alphabetic systems of West-European languages have different
quantity of letters, but in any case they are constructed according to signs or
graphical symbols of Latin alphabet.
For example, alphabets of Italian and English languages have 26 letters, or
contemporary German language has alphabetic system of 30 characters if to
consider symbols of letters with diacritical signs and ligatures. But however
all alphabetic systems of Western Europe have characters of Latin alphabet which
initially had 21 letters, that is shown on the chart.
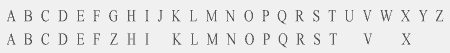
Letter Z has been excluded on 312 year BC.
Graphical symbol G is added in place of former letter Z on 234 year BC.
Letters Y and Z are added in the end of alphabet for words of Greek origin on
1st century BC.
Letters J and U are added on 16th century AD. But earlier sounds J and U was
designated by means of letters I and V.
Letter W is added for German languages.
And also some other alphabetic signs for designations of varied phonetic
soundings of vowels and consonants in different West-European languages have
been added.
As a result of historical development and consecutive changes of alphabetic
structure contemporary alphabets of West-European languages were generated, but
however the primary source were Latin letters which in essence are derivative
from symbols of ancient Phoenician writing. Therefore letters of contemporary
languages and Latin alphabet can be correlated to circular matrix of Phoenician
writing, as well as alphabetic signs of Greek alphabetic system, that is shown
on charts.
In scientific linguistics and among researchers of ancient civilizations
there is a hypothesis that Latin alphabet has been constructed according to
symbols of Etruscan writing. And actually there is an assumption that Etruscan
and Phoenician writings were equivalent ancient systems of letters according to
which alphabetic systems of Greece and Roman empire were formed.
And in essence it is possible to assume that Etruscan and Phoenician writings
have been coordinated with uniform circular matrix which has 11 numerical axes
and corresponds with numbers ancient duodecimal scale of mathematical notation
and numerology of forgotten civilizations.
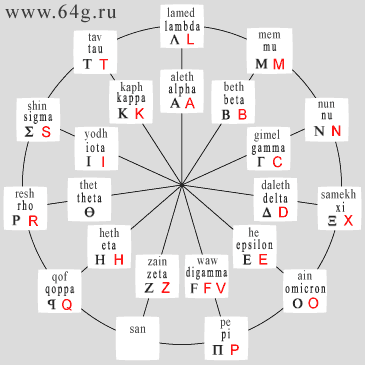
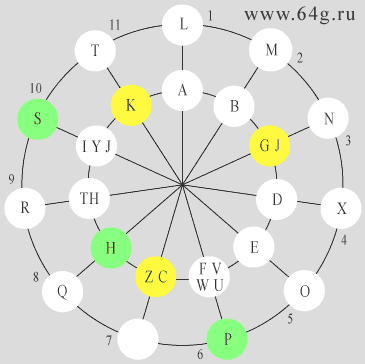
-
The left chart by dark color shows names or denominations of symbols of
Phoenician writing, and also names and graphical signs of Greek letters, and by
red color alphabetic characters of primary Latin alphabet. The right chart shows
characters of Latin alphabet, and also yellow and green colors allocate
positions of circular matrix where letters possess complex ratios of phonetic values.
Alphabetic character A - Greek alpha and Phoenician aleth.
This letter designated equivalent sound to Russian À in the Latin
alphabet, but now designates equivalent sounds to Russian À and Ý
in different West-European languages.
Alphabetic character B - Greek beta and Phoenician beth - equivalent
sound to Russian Á in the Latin alphabet and contemporary alphabetic
systems of West-European languages.
Character C designated equivalent sounds to Russian à and Ê
in the primary Latin alphabet, but now designates equivalent sounds to Russian
Ê Ñ × Ö in contemporary Latin based alphabets.
Takes the place of letter G and also corresponds with Greek zeta or Phoenician zain.
Alphabetic character D - Greek delta and Phoenician daleth - equivalent
sound to Russian Ä in the Latin based alphabets.
Alphabetic character E - Greek epsilon and Phoenician he.
Equivalent sound to Russian Ý in the Latin alphabet, but now designates
sounds equivalent to Russian È and Ý.
Alphabetic character F - Greek digamma and Phoenician waw - equivalent
sound to Russian Ô.
Greek letter digamma designated equivalent sound to English W, but Latin letter
F designates equivalent phoneme to Russian Ô, though Greek and Latin
graphical symbols are identical.
Character G has been added in Latin alphabet for designation of
equivalent sound to Russian Ã, but in contemporary alphabetic systems
also designates sound combination as Russian ÄÆ, and in essence has
accord with letter J.
Takes the place of letter C and corresponds with Greek gamma or Phoenician gimel.
Alphabetic character H - Greek eta and Phoenician heth - equivalent sound
to Russian Õ.
In some cases this graphical sign has no pronunciation. For example, digraphs PH
CH TH were applied in words of Greek origin instead of letters phi, chi, theta,
but in essence these digraphs were read in Latin language and read in
contemporary derivative alphabets without pronunciation H.
PH as equivalent sound to Russian Ï or Ô.
CH as equivalent sounds to Russian Ê or Õ, and × in the
English language.
TH as equivalent sound to Russian Ò.
Alphabetic character I - Greek iota and Phoenician yodh - equivalent
sound to Russian È.
Also equivalent sound to Russian ÀÉ in the English alphabet.
Character J has been brought in Latin alphabet for designation of long
sounding as Russian ÈÈ, but now this letter designates equivalent sound
to Russian É in contemporary West-European alphabets.
In some West-European alphabets designates equivalent phoneme to Russian ÄÆ
which has accord with letter G.
Alphabetic character K - Greek kappa and Phoenician kaph.
In the Latin alphabet this graphical sign designated phonetic equivalent of
Russian Ê, and it was used before vowel A unlike letter C which
designated the similar sound before vowels I and E.
Alphabetic character L - Greek lambda and Phoenician lamed - phonetic
equivalent of Russian Ë.
Alphabetic character M - Greek mu and Phoenician mem - phonetic
equivalent of Russian Ì.
Alphabetic character N - Greek nu and Phoenician nun - phonetic
equivalent of Russian Í.
Alphabetic character O - Greek omicron and Phoenician ain - phonetic
equivalent of Russian Î.
In words of English language this graphical sign also designates phonetic
equivalent of Russian ÎÓ that is similar to letter ÎÓÊÚ in the
Slavic alphabet of Cyril and Methodius.
Alphabetic character P - Greek pi and Phoenician pe - phonetic equivalent
of Russian Ï.
This graphical sign forms equivalent sound to Russian Ô in combination
with H, that is interesting as letters P and F are on one numerical axis in the
circular matrix.
Alphabetic character Q - Greek qoppa and Phoenician qof.
This graphical sign designates equivalent sound to Russian Ê and it is
used before vowel U, that forms common phonetic complex with letters K and C
which are used before vowels A I E.
Alphabetic character R - Greek rho and Phoenician resh - phonetic
equivalent of Russian Ð.
In some cases this letter has no pronunciation in words of contemporary European languages.
Alphabetic character S - Greek sigma and Phoenician shin - phonetic
equivalents of Russian Ñ or Ç.
This graphical sign in combination to letter H designates equivalent sound to
Russian Ø.
Alphabetic character T - Greek tau and Phoenician tav - phonetic
equivalent of Russian Ò.
In various contemporary alphabets there are phonetic equivalents to Russian Ö
× Ø in some cases in combination to letter I.
Character U has been brought in Latin alphabet for designation of
equivalent phoneme to Russian Ó, and before this sound of speech was
designated by letter V.
Alphabetic character V - phonetic equivalent of Russian Â.
Letters V and F designate conformable phonemes which correspond with Greek
digamma and Phoenician waw.
Alphabetic character W is connection or ligature of letters VV or UU
which designate equivalent sound to Russian ÓÎ.
Letters F V U W correspond with common position in the circular numerological matrix.
Alphabetic character X - Greek xi and Phoenician samekh - phonetic
equivalent of Russian ÊÑ.
Character Y has been brought in Latin alphabet on 1st century BC for
words of Greek origin and applied on a place of Greek upsilon which designated
phoneme as Russian Þ.
In contemporary alphabets in most cases this letter designates phonemes as
Russian È or É.
Also this letter takes common position with I and J in the circular
numerological matrix.
Alphabetic character Z - Greek zeta and Phoenician zain.
It is possible to assume that this letter initially meant phonetic equivalent of
Russian ÄÇ, but has been excluded on 312 year BC. And then in 1st century
BC it is brought in Latin alphabet for words of Greek origin and designation of
phonetic equivalent of Russian Ç, namely this letter was applied on a
place of Greek zeta.
Also this letter has common position with C.
Positions of letters C, G, K in the shown circular numerological matrix form the
spatial figure which is symmetric concerning seventh numerical axis, that is
noted by yellow color.
Letters C and K - identical phonetic equivalent of Russian Ê.
Letters G - phonetic equivalent of Russian à which before was
designated by letter C.
Letters C, G, K - conformable sounds as Russian Ê and Ã.
Positions of letters S, P, H form the spatial figure which is symmetric
concerning eighth numerical axis, that is noted by green color. Combination of
alphabetic signs SH and PH in this figure designate sounds as Russian Ø and Ô.
If to correlate combination of alphabetic signs CH to the empty position on
seventh numerical axis then it is possible to see one more spatial figure which
is formed by positions of letters T S TH H CH P, and which is symmetric
concerning third numerical axis.
And also in the shown circular numerological matrix it is possible to see some
other phonetic ratios which are connected with symmetric positions of letters
and correspond to various combinations of alphabetic symbols in words of
different West-European languages. Or otherwise to tell correspond to various
rules of writing orthography of words in different languages in which phonemes
of speech are designated by Latin letters and combinations of characters.
The shown circular matrix can be used for numerological calculations of
numerical meanings of words or human names. Namely it is possible to correlate
letters in words of different West-European languages to 11 numerical axes of
the shown matrix, and as a result it is possible to correlate words or names of
people to numbers of duodecimal numerology.
Look detail information about methods of
numerological calculations, and also about
mystical meanings and esoteric senses of
11 numbers of duodecimal numerology on pages of this website in section which
has the name: metalinguistics.
And also look in the section about metalinguistics
significant information on the method of numerological calculations of
duodecimal numerical values of words and names
by means of phonetic transcriptions which are written by letters of contemporary
Russian alphabet.
Different methods of calculations in numerology can yield unequal results, but
it is necessary to consider that this page shows circular matrix in which
spatial positions of six vowel letters of Latin alphabet are ambiguous or
otherwise to tell hypothetical, because symbols of Phoenician writing designated
20 consonants and only 2 vowel phonemes of speech.
Actually it is possible to assume that calculations by means of the shown
circular matrix are valid for ideal alphabet according to which letters
correspond to 20 consonant and 2 vowel phonemes of speech. And also according to
which letters form correct spatial figures or otherwise to tell absolute
geometrical configurations which are symmetric concerning eleven numerical axes.
If such ideal alphabet existed in the past or can be real in the future.
Following page shows ratio of Cyrillic letters of the Slavic alphabet with circular matrix of Phoenician writing, or otherwise to tell with universal numerical matrix of duodecimal numerology.
Also on following pages there is information about graphical symbols of sounds and mystical concepts of Cabbala, sacral true of three persons of the God and astronomical cycle of the planet Uranus, cosmological systems of human civilization and potentialities of universe in Greek myths, divine pantheon of mythology and celestial constellations of ancient Egyptian Decans.